Nuclear energy is being classified as a renewable energy source which is regarded as an option to replace fossil fuels: coal, gas, and oil. According to the World Nuclear Association there are currently 450 nuclear power reactors commercially operating in 31 countries worldwide, providing an estimated 10% of our world ́s electricity. Despite being classified as a fossil-free source of energy, the World Nuclear Association states that there is a need to replace some of the oldest nuclear reactors worldwide, especially those that are coal-fired and contributing to greenhouse gas emissions by releasing carbon dioxide into Earth’s atmosphere. (World Nuclear Association 2017).
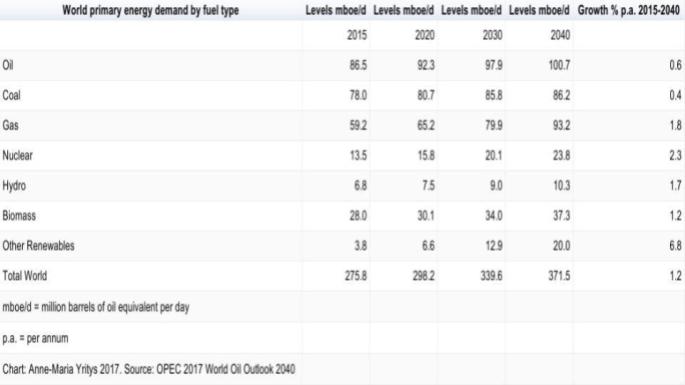
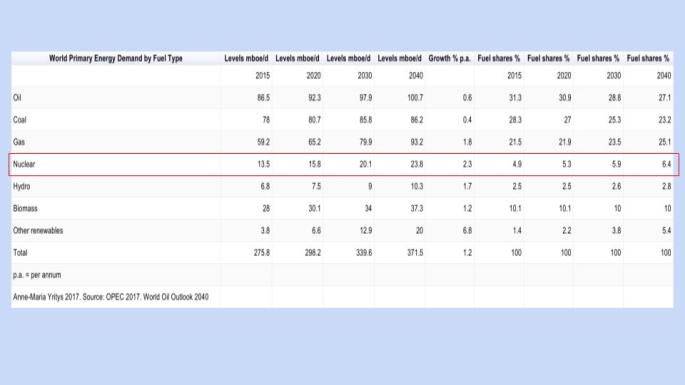
In IEA’s World Energy Outlook 2017, the International Energy Agency has a Sustainable Development Scenario for 2040 with forecasts where power generation has not been decarbonized despite the increase of low-carbon sources accounting for 40% of the total energy mix in 2040, and the worldwide usage of nuclear energy growing to 15% of the worldwide energy market. (International Energy Agency 2017). OPEC, in its World Oil Outlook 2040, estimates an annual growth rate of 2.3% for nuclear energy between 2015-2040. For more detailed information, see the table “World primary energy demand by fuel type” below.
With currently 12 countries getting around 25% of their electricity from nuclear power, France leads the statistics with 75% of its electricity coming from nuclear power. Beyond nuclear-friendly France, these countries are Hungary, Slovakia and Ukraine (more than 50% nuclear energy), Belgium, Bulgaria, Czech Republic, Finland, Slovenia, Sweden, and Switzerland (⅓ or more from nuclear power), Romania, Russia, Spain, UK, USA (around 20% from nuclear power), and Japan with around 25% of its electricity currently from nuclear power. Even some countries with no nuclear power plants, for instance Denmark and Italy, today depend to some extent upon nuclear energy. (World Nuclear Association 2019).
While the IEA forecasts that the share of nuclear energy on the worldwide market will grow to 15% of the total energy mix by 2040, OPEC estimates that nuclear energy will account for 6.4% of total world primary energy demand in 2040. See table “World Primary Energy Demand by Fuel Type” below.
The International Atomic Energy Agency IAEA, an autonomous organization under the UN established in 1957, works towards the strengthening of nuclear security worldwide, including the prevention of nuclear weapons and supporting countries in maintaining a peaceful, safe and secure usage of nuclear technology and science. Director General of IAEA, Yukiya Amano, states that nuclear energy, as one of the lowest-carbon technologies, helps countries in reducing their greenhouse gas emissions. While at first requiring large capital investments, nuclear power plants are known to be cost efficient. Moreover, as expressed by the IAEA, the new generation of nuclear reactors are constructed with improved performance, reliability and safety.
Learn more by watching WhatTheWhy ́s video “Nuclear Energy Explained: Risk or Opportunity”:
Nuclear Energy Explained: Risk or Opportunity?
How safe are nuclear power plants and nuclear power? Despite being classified as a renewable source of energy, nuclear power plants and nuclear waste pose a number of risks both to human beings, animals and our environment. In the case of an emergency and a nuclear plant accident (see for instance Tchernobyl or Fukushima), nuclear reactors can cause chemical explosions and release dangerous radioactive material. Even when normally functioning, nuclear power plants cause radioactive waste that has to be gotten rid of in some way. The solution for this has traditionally been to bury nuclear waste in deep geological repositories. (Harvard University 2016. Reconsidering the Risks of Nuclear Power).
While some countries (Australia, Austria, Denmark, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, Malaysia, Malta, New Zealand, Norway, Philippines, Portugal, and Switzerland) have completely abandoned or are about to completely abandon nuclear power plants and the usage of nuclear power, other countries continue to rely quite heavily on nuclear energy.
What are your thoughts about nuclear energy, the risks and safety of nuclear power (plants)?
You may also be interested in reading one of my previous articles: What Is The Future of The Worldwide Natural Gas Market?
Connect with me on Twitter @annemariayritys. For climate/environment-related posts only @GCCThinkActTank. Subscribe to Anne-Maria Yritys to receive my latest articles delivered personally to you.
